Stainless welding serves as a cornerstone skill in numerous industries, facilitating the fusion of stainless steel components to create resilient and enduring products. In this handbook, we embark on an exploration of the intricacies of stainless welding, elucidating common queries and offering expert guidance to empower you in mastering this indispensable craft.
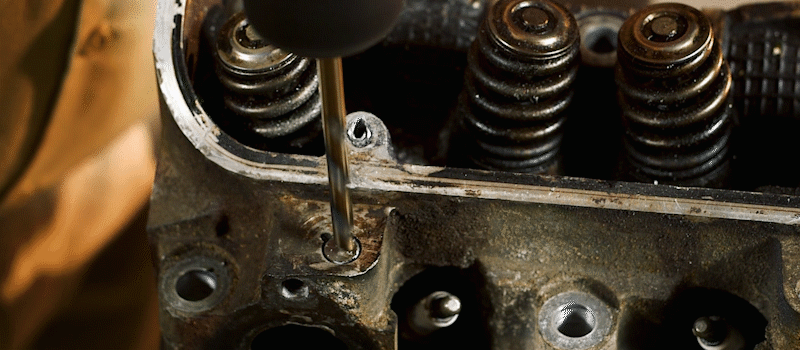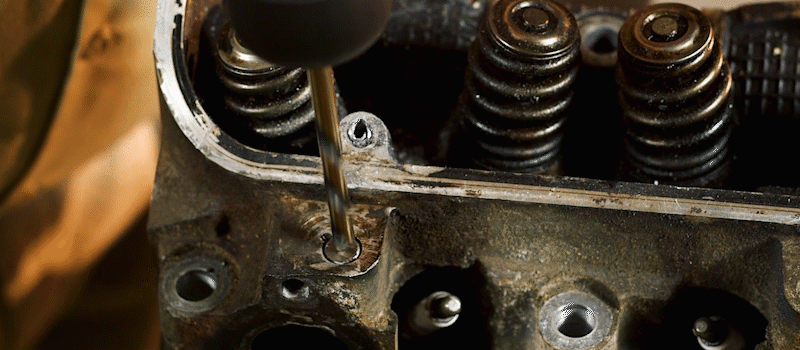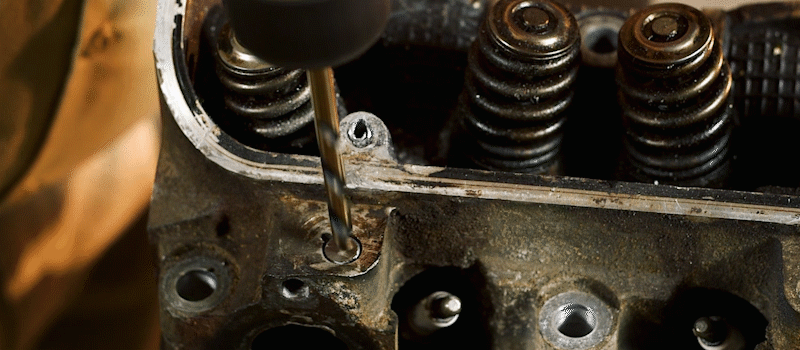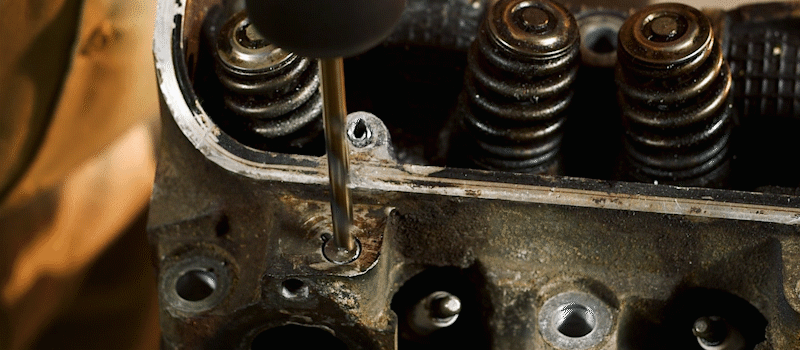
What factors should be considered before embarking on a stainless welding project?
Before commencing a stainless welding project, several factors must be carefully considered. Firstly, select the appropriate stainless steel grade for your application, considering the properties and weldability of different grades. Secondly, ensure you possess the necessary equipment, including a suitable welding machine, electrodes, and protective gear. Additionally, meticulously prepare the workpiece by thoroughly cleaning it to remove any contaminants that could compromise weld quality. Lastly, familiarize yourself with the welding technique required for the specific joint design and material thickness.
What challenges are commonly encountered during stainless welding, and how can they be overcome?
Stainless welding presents various challenges, such as distortion, overheating, and weld contamination. To address distortion, employ proper welding techniques such as back-stepping or clamping the workpiece. Overheating can lead to carbide precipitation and reduced corrosion resistance, so regulate heat input by adjusting welding parameters and using pulse welding when necessary. Preventing weld contamination requires maintaining a clean work environment and using suitable shielding gas, such as argon or a mixture of argon and CO2.
What methods of stainless welding are available, and when should each be utilized?
Several methods of stainless welding exist, each suited to different applications and requirements. Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding is ideal for thin materials and intricate welds, offering precise control over heat input and weld quality. Metal Inert Gas (MIG) welding is suitable for thicker materials and high-speed production, providing good penetration and deposition rates. Stick welding, or Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), is versatile and can be used in outdoor or adverse conditions where other methods may struggle. Choose the method that best fits your project’s specifications and your proficiency level.
How does geotextile contribute to stainless welding applications?
Geotextiles, permeable fabrics used in construction and civil engineering projects, often complement stainless welding applications. For instance, in environmental protection projects, geotextile materials are welded or sewn together using stainless welding techniques to create durable containment barriers for soil stabilization, erosion control, and drainage systems. The corrosion resistance and strength of stainless steel ensure the longevity and reliability of these critical applications.
Mastering stainless welding requires a blend of technical knowledge, practical skills, and attention to detail. By considering key factors before starting a project, addressing common challenges with appropriate techniques, understanding different welding methods, and recognizing the role of materials like geotextile, you can achieve high-quality welds that meet the demands of various industries. With dedication and practice, you can become proficient in stainless welding and contribute to the creation of durable and reliable structures and products.
modulation control valve
Modulation control valves continuously adjust flow to maintain a desired pressure, temperature, or other process variable. They offer precise, responsive control by varying the valve opening, making them useful for process control, HVAC, and other applications requiring modulating flow regulation.


